Introduction
In this post, you will learn what is NMap and how it works, Once you completely read this post by the end you will know how to work with NMap with a flow like a pro in NMap ✔…
Before getting into the commands and kinds of stuff, I have already written an Intro about NMap [Click here] to read.
Also Read: Network mapping using MASSCAN is easy if you read this ❤
Video:
What is NMap
Nmap stands for “network mapping“. The initial release of this software was in the year 1997. As I said Nmap is a network mapping tool, this particular tool comes under the scanning section. In simple words, Nmap is software that scans the network of a particular IP Address and displays the details of domains like the OS and firewall level securities.
The Nmap is available for all three OS like Linux, Mac, and also windows.
Advertisement
Who developed the NMap tool ❓
The author of the tool is Fyodor and he seems to former NSA guy but whatever, let’s talk about the tool. If you know more information about the NMap author comment down below.
Features in NMap
- Basic Nmap IP or host Scan
- Scan multi ports
- Save scan results to a .txt or xml file
- Scanning TCP or UDP ports
- How to find or detect the operating system
- Disabling DNS name resolution
- Get Information about HTTP services
- How to Scan the Firewall Settings on a Network Device
- Scan IPv6 Addresses
- how to determind Host Interfaces, Routes, and Packets etc.,
- Find the open port
- Check the number of packets send or received
- Detect service/daemon versions
- Scan for MAC address spoofing
- Launching DOS
- Launching brute force attacks
- Detecting malware infections on remote hosts
- Timing and Performance
Advertisement
Useful commands in NMap
-sL – just create a list of running hosts, but do not scan ports
-sP – only check ping
-PN – consider all hosts available, even if they do not respond
-sS / sT / sA / sW / sM – TCP scan
-sU – UDP scan
-sN / sF / sX – TCP NULL and FIN scan
-sC – run the default script
-sI – lazy Indle scan
-p – specify the range of ports for checking
-sV – a detailed study of ports to determine the version of services
-O – determine the operating system
-T [0-5] – scanning speed, the more, the faster
-D – mask scan using _ctitious IP
-spoof-mac – set your MAC address
How does the NMap work ❓
Follow every example carefully by end of thispost you will be very familiar with the tool and if you continuously work for 2 -4 hrs you will become a pro.
Work hard until you reach let’s make hand’s wet
BY STUPID ME ????
Example1, Standard scan
Let’s do a single host scan, which means we are just scanning for the target
nmap 10.10.10.1
0r
nmap google.com
You can enter either IP or just the target domain…
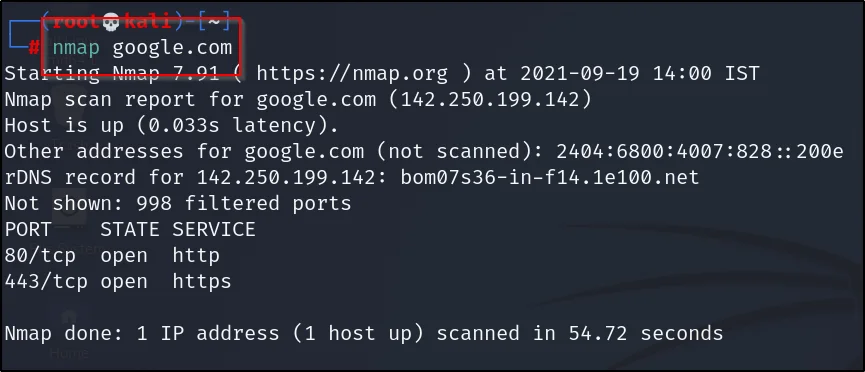
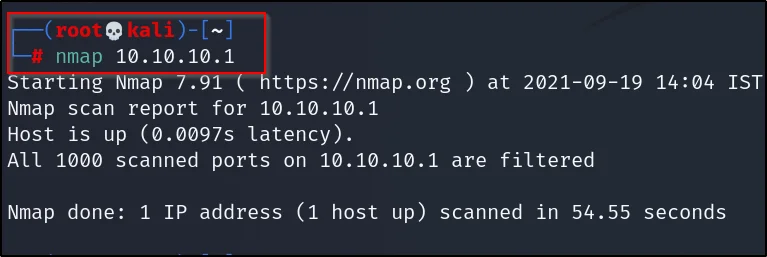
Example2, Subnet scan
In this example let’s scan for a subnet, this is the command ????
nmap 10.10.10.0/24

Example3, Scanning IP ranga
Let’s scan for an IP range between o to 100, just enter this command…
nmap 10.10.10.0-100
You could go all the way to 256 and not beyond that hope you listen in networking classes
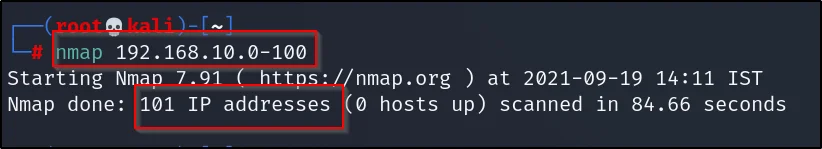
Example4, Scanning from file list
Scanning the list of IP addresses saved in a file,
nmap -iL <file name>
nmap -iL ip

Example5, Scanning multiple IP manually
Scanning for multiple IP addresses, just do this way
nmap 10.10.10.1 192.149.168.1 192.122.122.1
I have left a gap between every specific IP I wanna scan
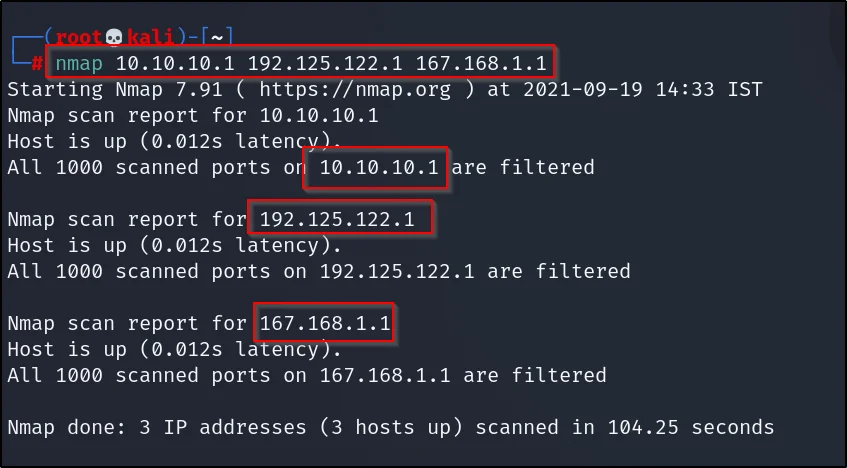
Example6, Full port scan
Let’s scan for specific ports
*NOTE, By default the nmap can scan up to 1000 ports and if you wanna scan all the ports enter
nmap -p- google.com or nmap -p- 142.250.66.14
-p- is scanning entire ports
Between TCP and UDP, there are only 65533 ports…

Example7, Multiple port scan
Scanning for specific and particular ports
nmap -p 80,88,443 scanme.nmap.org or instead of subdomain enter the IP
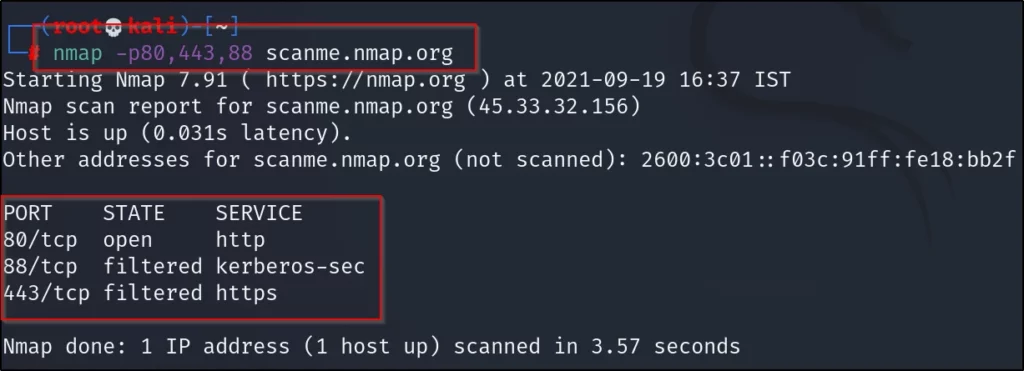
Advertisement
NMap Example8, Scaning for service
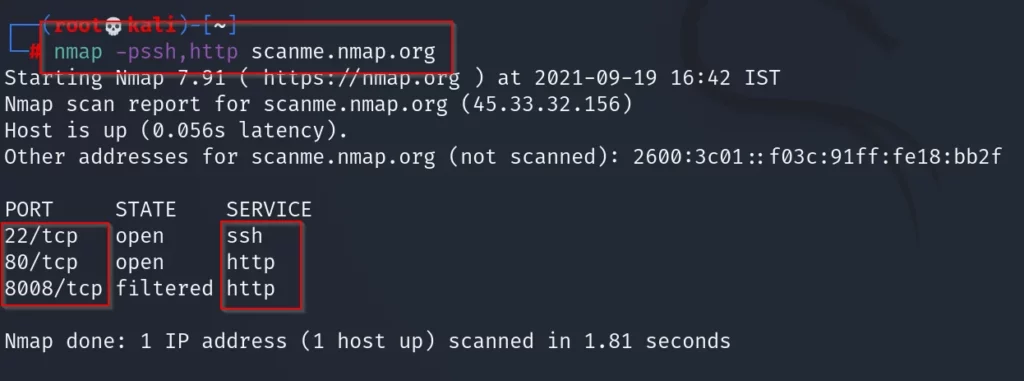
Suppose if you don’t know the ports just enter HTTP or ssh whatever you particularly searching for in target…
The command is something like this ????
Nmap -phttp,ssh scanme.nmap.org
Example9, SYN TCP Scan
From examples 9 to 13 we are going to different types of nmap scan are like SYN, TCP, UDP and a few more.
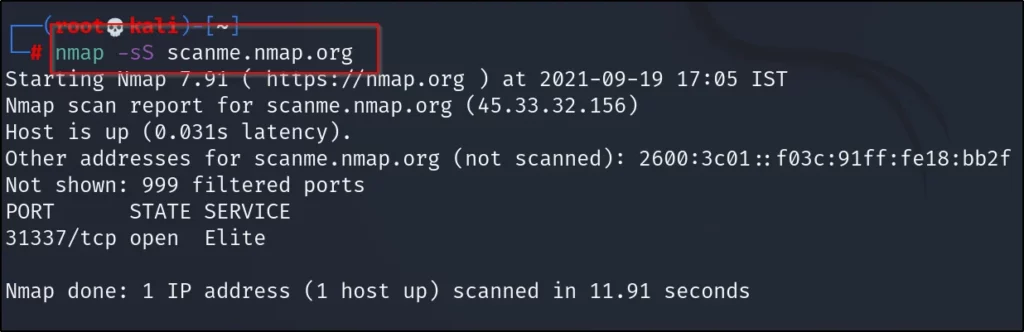
In this example let’s see about TCP SYN scan and most of the time you will use this, so pay attention
nmap -sS scanme.nmap.org or nmap -sS 45.33.32.156
Example10, Full TCP Scan
Doing a full TCP scan
nmap -sT scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -sT 45.33.32.156

Example11, Full UDP Scan
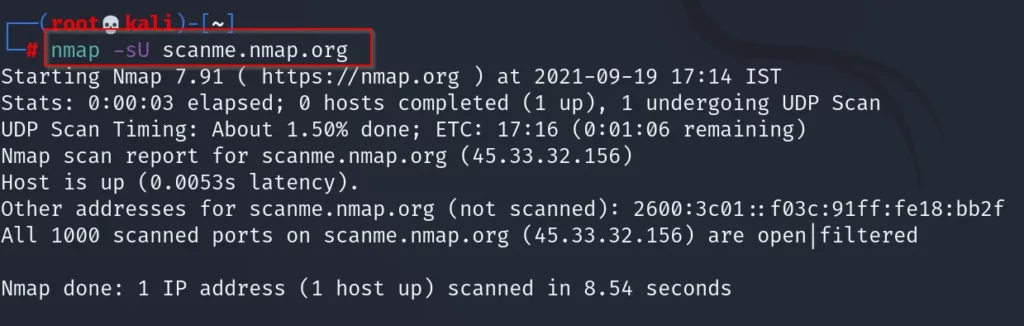
Let’s do UDP scan
nmap -sU scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -sU 45.33.32.156
By default, it scans for 1000 ports only as I mentioned before ????
Example12, Ping scan
Doing a ping scan
nmap -sP scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -sP 45.33.32.156

Example13, Not doing ping scan assuming every host are up
Now, we are not pinging the host assume every host is up
nmap -Pn scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -Pn 45.33.32.156

Example14, Service version scan
Now, let’s search for the service and version of the target and if you want go take some break
nmap -sV scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -sV 45.33.32.156
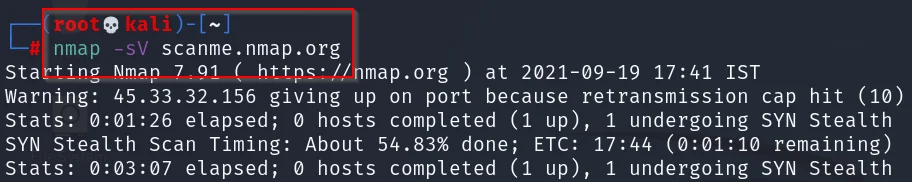
For me it took so late, you keep on trying and be chill until the result ????
Example15, Operating system scan
Finding only the Operating system
nmap -O scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -O 45.33.32.156

Example16, -A Scan
In this example let’s find OS & the service and version of the target which means instead of the above two commands you could do this single command
nmap -A scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -A 45.33.32.156

The scan for the first time will be pretty slow ⏳
NMap Example17, Time scan
When you work with nmap it is like working with a turtle, no offence but it is true the scan is dead slow in nmap so, to speed up any scan use this command
nmap < whatever command you enter here> -T0 <IP address or tagret subdomain>
nmap -p80,443 -T0 scanme.nmap.org
Instead of -T0, you could add, it is not O it is zero
-T0: slow
-T1: sneaky
-T2: polite
-T3; normal time
-T4: aggressive
-T5: very aggressive
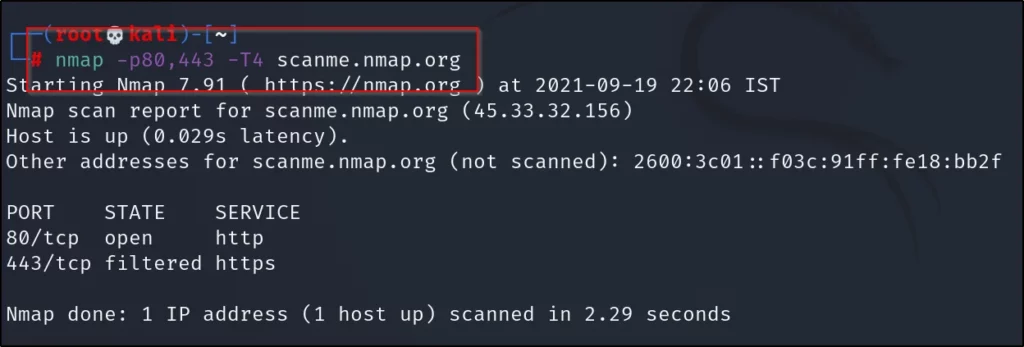
I used -T4 you could enter whatever time you wanna but better to go with -T4
Example18, ICMP Scan
Doing ICMP (internet control message protocol) echo packets to discover any host
nmap -PE scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -PE 45.33.32.156

Advertisement
NMap Example19, Saving results
Jesus christ ???? I am tired of writing okay anyways let me continue
Now, let’s do save the scan in any format you want
If you wanna save in normal text then use this command
nmap -p80 -oN save scanme.nmap.org (or) nmap -p80 -oN save <IP address>
here save is the file name, you enter whatever you want

Instead of -oN you can enter the below ones
-oG: Grepable file
-oX: XML file
-oA: Most used one (saves the output in all formats)
NMap Conculusion:
According to my knowledge somewhere in the cerebral area, this is the best Network scanning tool and there may be alternatives like masscan and angryip but this is the best…????❤
Advertisement
Also Read: Recon-ng full tutorial, and the best one ????
Also Read: How to install custom kali in VM ware workstation player




