Introduction
In this post, you will learn how to download ARP-SCAN and once you completely read the post you will become a pro in arp-scanning. Before entering into a topic I have one best alternative for address resolution protocol-SCAN it’s is netdiscover tool, We will talk about netdiscover in another post.
Video:
What is ARP-SCAN?
The ARP-SCAN is an internal network scanning tool. Comparing it to netdiscover arp-scanning is very much faster. This tool can noisily gather information about internal networks. When I say noisy, the tool will be caught by the IDS and IPS sensors and leave traces behind.
Advertisement
How to download ARP-SCAN?
ARP-SCAN stands for Address Resolution Protocol scanning and from now on we are going to use address resolution protocol-scan. The arp-scanning is Linux based tool and by default, the tool is available in most of the Linux distros
If the arp-scanning is not available in your Linux machine. Just follow the below steps.
Open terminal > enter > Sudo arp-scan get install
If you are already in the root then you don’t need to use root. so, done congratulation!!! You successfully installed address resolution protocol -scan.
Also Read: Three different ways to do password cracking
Advertisement
Who developed arp-scan?
The arp-scan was developed by royhills and this is guy is from London, UK and he has also developed other notable tools like ike-scan and we will see a full tutorial on ike-scan.
You could also download the address resolution protocol-scan from the official page and follow the instructions.

arp-scanning all commands?
- –help or -h: Display this usage message and exit.
- –file or -f: Read hostnames or addresses from the specified file instead of from the command line. One name or
IP address per line. Use “-” for standard input. - –localnet or -l: Generate addresses from the network interface configuration.
- –timeout= or -t: Set initial per-host timeout to ms, default=500.
- –interval= or -i: Set minimum packet interval to <x>.
- –bandwidth= or -B: Set desired outbound bandwidth to, default=256000.
- –verbose or -v: Display verbose progress messages.
- –version or -V: Display program version and exit.
- –quiet or -q: Only display minimal output.
- –plain or -x: Display plain output showing only responding hosts.
- –ignoredups or -g: Don’t display duplicate packets.
- –rtt or -D: Display the packet round-trip time.
- –pcapsavefile= or -W: Write received packets to pcap savefile.
- There are much more commands but mostly these commands are enough and if you wanted to see all the commands just type arp-scan –help
Advertisement
How arp-scan works?
arp-scan works in a really noisy way and it goes and asks the network for the target you are searching for, when I say it is noisy that means leaves behind traces.
Also Read: How to change MAC address in kali linux
Example1: Local scan
In example 1 we are going to find the internal networks running.
sudo arp-scan -l

Example2: MSC scan
Now, we are going to see the MAC address of eth0 of the subnet mask
sudo arp-scan -a

Example3: Subnet
Scan an IP network with the custom subnet.
sudo arp-scan IP address / port
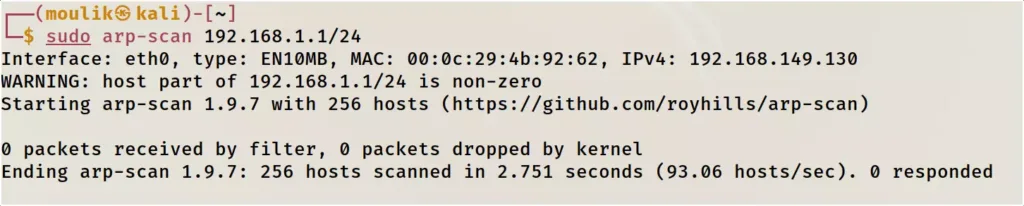
*sorry for the colour change
Example4: All in one scan
scanning a custom MAC address with a subnet
sudo arp-scan -I eth0 --srcaddr=macaddress ipaddress/port
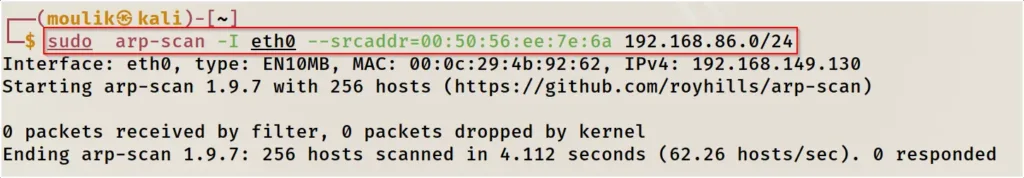
Conclusion
I hope the post helped you a lot and other commands in this tool are simply waste and as the tool is very noisy I suggest one go with netdiscover tool and to know more about netdiscover tool visit the hacking tool menu.
Advertisement
Also Read: Three most ways to compromise a device




