Introduction
In this post, you will learn about the dirb tool and we will see some of the most used commands in this tool and also below is the video format of the post, check it out 👇🏾
Video:
What is dirb❓
Dirb is a web application analysis tool and even you can do brute forcing on the target using the tool. “But hey, wait my professor used to say brute-forcing is dangerous than selling drugs“
There is a high chance for a hacker to get caught while using the brute force technique. This tool works by launching a dictionary-based attack against a web server and analyzing the response.
So, while talking about brute-forcing we need a set of usernames and passwords and this tool comes with the list of usernames and passwords.
You can find the list here
cd /usr/share/wordlists/dirb
Advertisement
Where to download dirb
Use the below link to download the tool and if you are a kali Linux user then the tool must be pre-installed. Anyways to install the tool in kali Linux use this command.
apt-get install dirb
Useful commands in dirb
-a: Specify your custom USER_AGENT.
-c: Set a cookie for the HTTP request.
-f: Fine tunning of NOT_FOUND (404) detection.
-H: Add a custom header to the HTTP request.
-i: Use case-insensitive search.
-l: Print “Location” header when found.
-N: Ignore responses with this HTTP code.
-o: Save output to disk.
-p: Use this proxy. (Default port is 1080)
-P: Proxy Authentication.
-r: Don’t search recursively.
-R: Interactive recursion. (Asks for each directory)
-S: Silent Mode. Don’t show tested words. (For dumb terminals)
-t: Don’t force an ending ‘/’ on URLs.
-u: HTTP Authentication.
-v: Show also NOT_FOUND pages.
-w: Don’t stop on WARNING messages.
-X / -x: Append each word with these extensions.
-z: Add a milliseconds delay to not cause excessive Flood.
Advertisement
How to use the dirb tool
To be a pro in using the dirb tool make sure you follow the examples below properly and If you have any doubt comment down below and watch the video I made on the tool.
Example 1, Doing standard scan in dirb
To do a standard scan use this command
dirb <target>
dirb http://45.33.32.156
Example 2, Enumerating directory with extension list
You should take a look at the below screenshot for sure and then you will understand we are enumerating the .php for the login page of the target.
dirb http://target/ -X .php
-X / -x: Append each word with these extensions.

Example3, Save the output
To save the output in a file, just use this command
dirb http://192.168.1.106/ -o output.txt
-o: Save output to disk

Example4, Bypassing If any errors found
Bypassing any errors are found while scanning, to do so, use the below command.
dirb http://192.168.1.106/-N 302
-N: Ignore responses with this HTTP code.

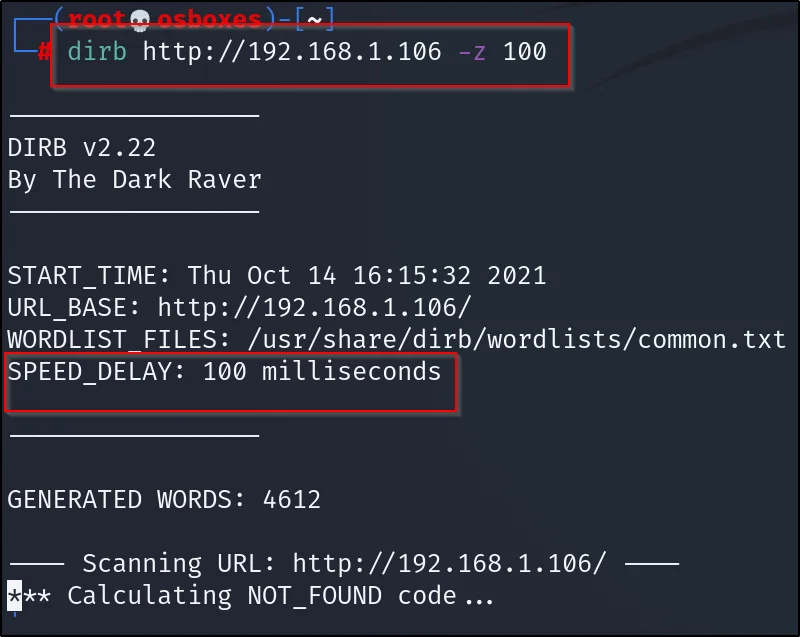
Example 5, Adding speed for the scan
You can delay the scan to get a deeper detailed scan. And below is the command for speeding up the scan.
dirb http://192.168.1.106 -z 100
Conclusion
By, Now you should be familiar with the dirb tool and check my youtube video on dirb, there are more commands and explanations.
Advertisement
Also Read: Burpsuite full tutorial for beginners
Also Read: F-string in python




